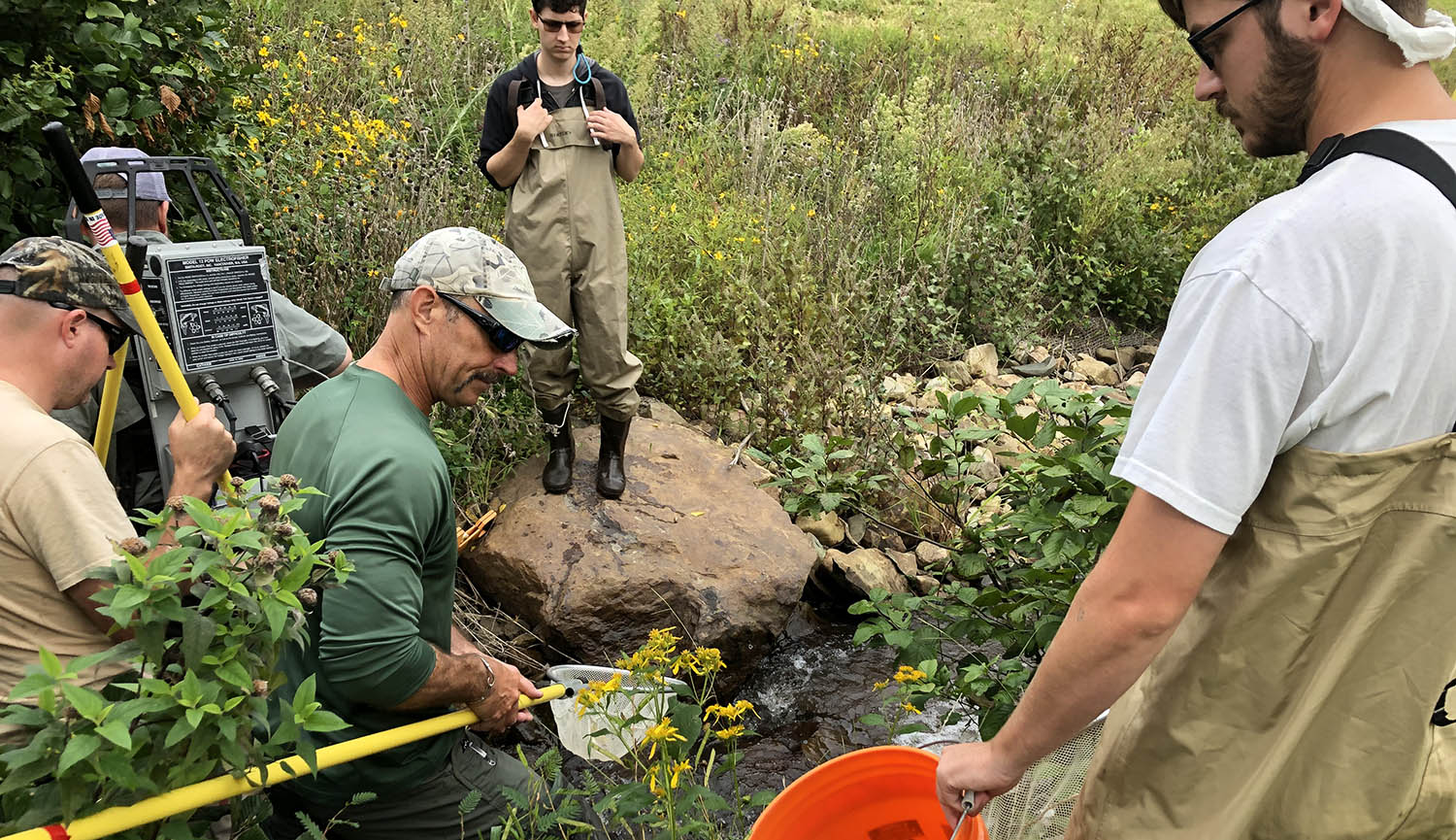
Find out about recent fish counts.
Restoring Connections
Eliminating barriers and disruptions. The job of our rivers naturally is to move the mountains to the sea. Dams and other barriers like culverts can disrupt natural stream flow, disconnect fish and wildlife habitat, and impair water quality. Removing unnatural barriers and disruptions is particularly important for conserving our waterways.
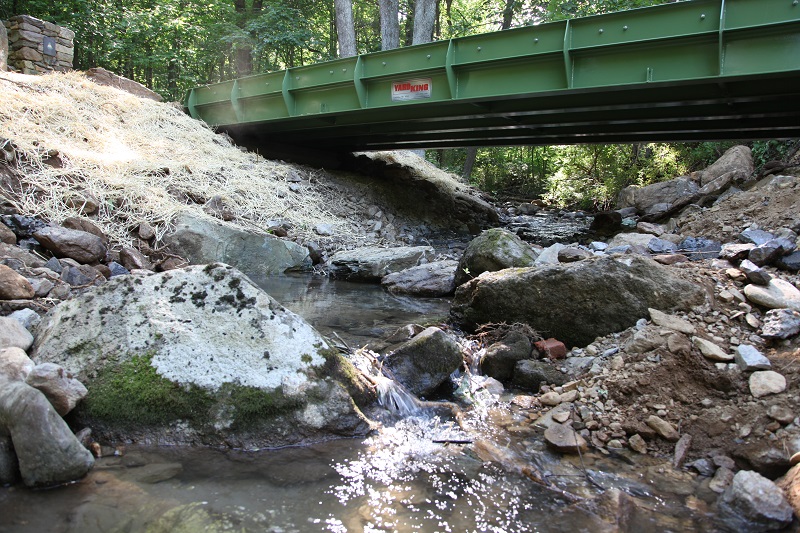
A Fish Runs Through It
As the fog broke on a brisk November morning in Madison County, more than three dozen people arrived at the Whiteoak Canyon trailhead ready to celebrate the new, 35-foot, open-span bridge over Cedar Run. They marveled at the sounds of water bubbling over the rocky streambed from the north side of the bridge to the south. Many walked upright beneath the sturdy, brown, steel-framed structure. And all excitedly searched the deep pools for our guests of honor—the native brook trout, a species of concern on Virginia’s Wildlife Action Plan.
Whiteoak Canyon Trailhead
SYRIA, VA: The new 35-foot span bridge across Cedar Run offers hikers and nature-loving community members improved access to the popular Whiteoak Canyon trailhead and opening up three miles of stream habitat to native fish for the first time in decades. The effort is a public-private partnership between Shenandoah National Park, The Piedmont Environmental Council, Trout Unlimited, and the local landowners, the Graves family.
Free Flow
PEC has taken on the work of restoring local rivers by removing culverts and low-water crossings that can be roadblocks to stream health. By replacing these barriers on roads and driveways with fish- friendly designs, we are improving habitat and water quality.
Many aquatic species, including Virginia’s state fish, the Eastern brook trout, benefit from these restoration projects. Ideally, we hope these projects will influence government agencies to incorporate fish-friendly designs as they update roads and stream crossings.

Eastern Brook Trout Monitoring Protocols for Headwater Streams in Virginia’s Piedmont
During the summer of 2017, PEC Fellowship participants Dana Ek and Callee Manna put together this stream monitoring guidebook as part of their final practicum project. The guidebook is meant to serve as a reference for PEC and other entities who are planning of stream restoration projects, especially in the development of improved monitoring procedures.
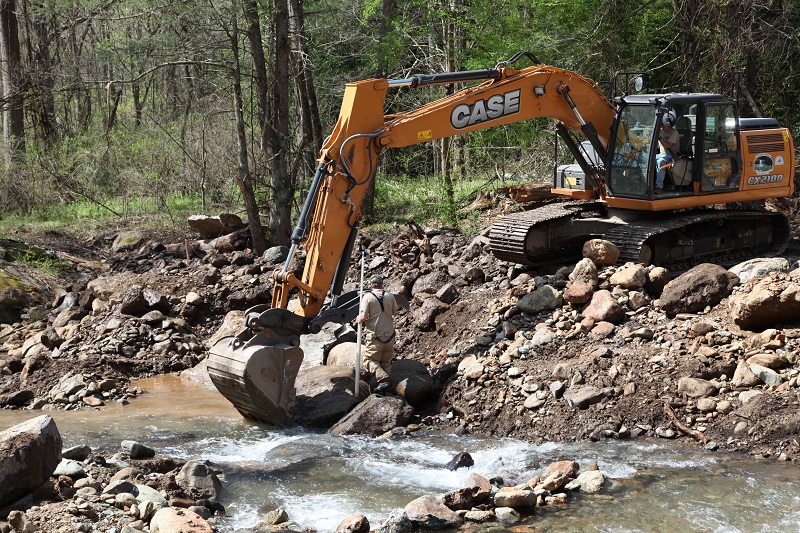

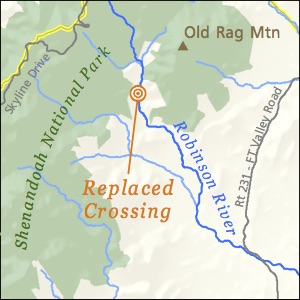
Robinson River
SYRIA, VA. At the Robinson River, 350 linear feet of stream was restored to its natural channel, stabilizing banks from erosion, and ultimately removing sediment from going downstream to the Chesapeake Bay. In all, 5.3 miles of habitat was restored for aquatic species such as American eel and brook trout. PEC worked with USFWS, Shenandoah Streamworks, Trout Unlimited, and local landowners to complete this stream restoration project in April 2017. Monitoring for water quality, and fish population health with the help of partners of VA DGIF and TU.

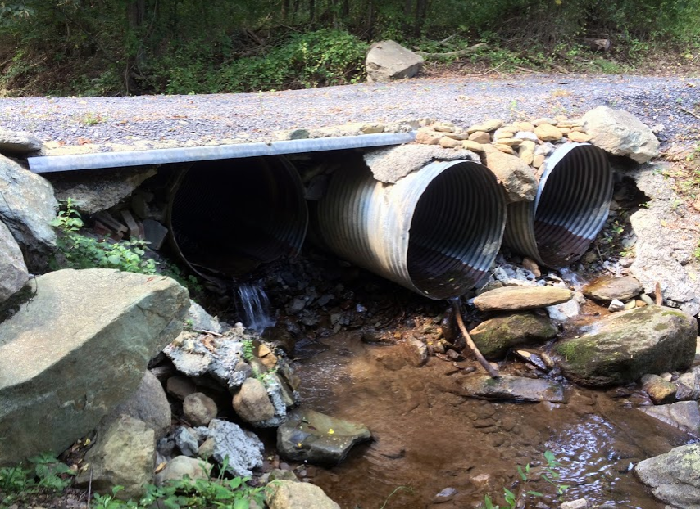
Sprucepine Branch
HUNTLY, VA: Recent work at Sprucepine Branch reconnected 2 miles of stream, as a set of culverts were removed from a private driveway, and replaced with a bridge. PEC coordinated with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and Shenandoah Streamworks on the natural channel design and construction. The work included re-grading stream banks and in-stream structures that restored the natural hydrology of those streams.
The Virginia Department of Game and Inland Fisheries provided pre and post fish community monitoring.

Restoring Connections – By Eliminating Barriers
Culverts, low-water crossings and linear infrastructure (i.e. pipelines, highways) can serve as disruptions to healthy stream flow.

Good News for the Brook Trout
We’re continuing our efforts to increase the habitat available to the eastern brook trout and other fish species with two pilot culvert removal projects…
Teaming Up to Save the “Brookie”
Virginia’s state fish, the eastern brook trout, is in trouble. The Commonwealth’s only native trout has seen a sharp decline in population due to a detrimental combination of rising temperatures, physical barriers to streamflow, pollution, and habitat loss. Many expect the species to be added to VA’s Wildlife Action Plan list in the near future.


